Understanding One-to-Many Relationship Between Orders and OrderDetails
×
Join our community on Telegram!
Join the biggest community of Pharma students and professionals.
Understanding One-to-Many Relationship Between Orders and OrderDetails
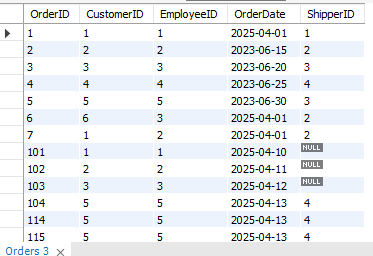
Orders Table:
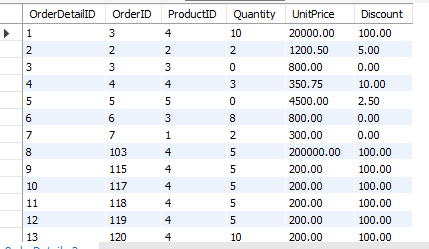
OrderDetails Table:
Query Explanation:
● There is a One-to-Many relationship between Orders and OrderDetails – one order can have multiple order detail entries.
● The OrderID in the OrderDetails table acts as a foreign key, referencing the OrderID in the Orders table.
● This follows proper normalization practices (typically 2NF), where details like quantity and unit price are separated from the order header.
● The INNER JOIN is used to combine rows from both tables where the OrderID matches, returning complete details of each product in the order.
SQL Query:
-- Creating Orders table
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID INT,
OrderDate DATE
);
-- Creating OrderDetails table with foreign key referencing Orders
CREATE TABLE OrderDetails (
OrderDetailID INT PRIMARY KEY,
OrderID INT, -- Foreign key to establish One-to-Many relationship
ProductID INT,
Quantity INT,
UnitPrice DECIMAL(10,2),
FOREIGN KEY (OrderID) REFERENCES Orders(OrderID)
);
-- Joining Orders and OrderDetails to fetch complete order info
SELECT
Orders.OrderID,
Orders.OrderDate,
OrderDetails.ProductID,
OrderDetails.Quantity,
OrderDetails.UnitPrice
FROM
Orders
INNER JOIN
OrderDetails ON Orders.OrderID = OrderDetails.OrderID;
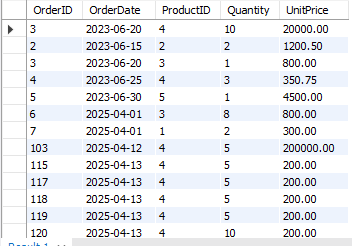
Output: