Explain 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF Using Your Tables
Join our community on Telegram!
Join the biggest community of Pharma students and professionals.
Explain 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF Using Your Tables
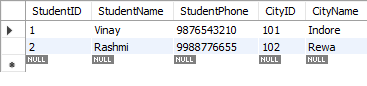
Table: StudentCourses (Before 1NF)
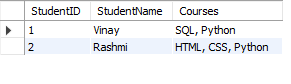
Table: Students (2NF)
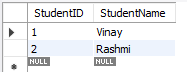
Students Table:
Query Explanation:
-
Step 1: We create the
StudentCoursestable and insert data, where multiple courses are stored in a single column for each student. This violates the 1NF rule of atomicity. -
Step 2: We convert the table into 1NF by creating the
StudentCourses_1NFtable, where each course is placed in a separate row for each student, ensuring that every column contains atomic values. -
Step 3: We create a separate
Studentstable to eliminate partial dependency and meet the requirements of 2NF. In this step, we ensure thatStudentNamedepends solely onStudentID(not on the courses). -
Step 4: The
StudentCoursetable is created to establish a many-to-many relationship betweenStudentIDandCourse. This helps meet the 2NF requirement, as the primary key is a combination ofStudentIDandCourse. -
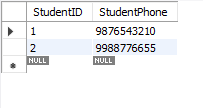
Step 5: The
StudentPhones_3NFtable is created, where student phone numbers are stored separately to remove any transitive dependency betweenStudentPhoneand other non-key attributes. This ensures that the table is in 3NF.
Result:
You can copy-paste this entire block and run it in your SQL editor to create and populate the tables for 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF in one go.
SQL Query:
-- Step 1: Creating the original table (StudentCourses)
CREATE TABLE StudentCourses (
StudentID INT,
StudentName VARCHAR(50),
Courses VARCHAR(100)
);
-- Inserting sample data into StudentCourses table
INSERT INTO StudentCourses VALUES
(1, 'Vinay', 'SQL, Python'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'HTML, CSS, Python');
-- Step 2: Creating the StudentCourses_1NF table to convert to 1NF
CREATE TABLE StudentCourses_1NF (
StudentID INT,
StudentName VARCHAR(50),
Course VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Inserting data into StudentCourses_1NF
INSERT INTO StudentCourses_1NF VALUES
(1, 'Vinay', 'SQL'),
(1, 'Vinay', 'Python'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'HTML'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'CSS'),
(2, 'Rashmi', 'Python');
-- Step 3: Create Students table for 2NF
CREATE TABLE Students (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY,
StudentName VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Inserting data into Students table
INSERT INTO Students VALUES
(1, 'Vinay'),
(2, 'Rashmi');
-- Step 4: Create StudentCourse table for 2NF
CREATE TABLE StudentCourse (
StudentID INT,
Course VARCHAR(50),
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, Course),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Students(StudentID)
);
-- Inserting data into StudentCourse table
INSERT INTO StudentCourse VALUES
(1, 'SQL'),
(1, 'Python'),
(2, 'HTML'),
(2, 'CSS'),
(2, 'Python');
-- Step 5: Create StudentPhones_3NF table for 3NF (StudentPhone in a separate table)
CREATE TABLE StudentPhones_3NF (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY,
StudentPhone VARCHAR(15),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES StudentCourses_1NF(StudentID)
);
-- Inserting data into StudentPhones_3NF table
INSERT INTO StudentPhones_3NF (StudentID, StudentPhone)
SELECT StudentID, '9876543210' FROM StudentCourses_1NF WHERE StudentID = 1;
INSERT INTO StudentPhones_3NF (StudentID, StudentPhone)
SELECT StudentID, '9988776655' FROM StudentCourses_1NF WHERE StudentID = 2;
Output:
Converted Table: StudentCourses_1NF
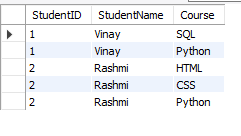
Table: StudentCourse (2NF):
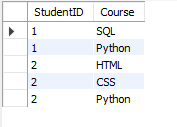
Table: StudentPhones_3NF